NATIONAL HEALTHCARE SYSTEMS
What is already known about the subject?
- The member states of the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) develop primary health care as a priority, improving existing and implementing novel management solutions.
- Most CIS countries apply the territorial-district principle, but the "radar" principle based on the concept of "case of disease" is still used in management.
What might this study add?
- The analysis of the management characteristics of primary health care subsystems in the CIS countries showed a certain and varying degree of their readiness for continuous and constant healthcare provision throughout the life — the principle of permanence (as we propose to call it).
Based on an analytical review of information sources on the status and development of various aspects of primary health care (PHC) in the world and in selected countries, as well as international evidence-based recommendations in a series of reviews, to assess international experience and guidelines for the development of PHC in selected members of the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS), in particular, with respect to the management aspect. To prepare the review, a database of publications, regulatory legal documents and Internet resources was used based on selected keywords and concepts related to the management of PHC and its characteristics. Priority was given to last decade materials concerning the CIS member states. The characteristics of national PHC management were identified, systematized and arranged in following sections: principles of PHC subsystems, structural elements, processes.
The second part presents the analysis of the development of PHC management and its characteristics, including the implementation of recommendations with proven effectiveness in the CIS member states. The analysis of sources on the experience of the CIS member states in the medical examination and follow-up of patients with chronic diseases gave grounds to propose a more precise name for continuous health care in managing health throughout life — the principle of permanence.
EXPERT COUNCIL
The article presents an expert consensus statement on modern approaches to the management of patients with chronic bronchitis. The document emphasizes an interdisciplinary strategy for patient management, including risk factor modification, follow-up care, and prevention. Experts highlighted the importance of smoking cessation, vaccination, and individualized pharmacotherapy, including mucolytics and bronchodilators. The role of antibacterial therapy during exacerbations and the need for standardized follow-up approaches are also discussed. The consensus resulted in guidelines aimed at improving the quality of life of patients with chronic bronchitis and preventing disease progression.
SCIENTIFIC NOVELTY
What is already known about the subject?
- The spread of overweight and obesity is a global problem affecting both the adult population and children and adolescents aged 5 to 19 years.
- The search for problem solutions requires an integrated approach that covers medical, economic and socio-psychological aspects.
What might this study add?
- The understanding of the attitude of young people to overweight has been expanded, and the influence of body weight on individual, social and professional skills of a person has been determined.
- The study results indicate the need to search for new strategies of influence and persuasion.
Aim. To study the attitude of young people to excess body weight (EBW), its causes and consequences, as well as the level of readiness to maintain normal body weight.
Material and methods. The article analyzes publications and studies on excess body weight as a complex medical, social and psychological problem. The following databases were used: Scopus, CyberLeninka. The study used sociological (online questionnaire) and analytical (interpretation of research data) methods. The empirical basis was an original sociological study of students aged 18 to 35 years, conducted in November 2023 in 7 universities and 8 colleges of the Saratov region. The total sample size for all study stages was 4 852 people.
Results. Young people are well aware of the problem of excess weight (81,6%), which is determined by an unhealthy lifestyle (81,1%), unwillingness to monitor weight (66,5%), a large amount of offered and available fast food and drinks (55,5%). Excess weight is caused by overeating (80,6%), stress (75,8%), beer alcoholism (67,7%) and endocrine diseases (53,1%). The reasons forcing a person to monitor body weight were possible health problems (83,1%) and loss of physical attractiveness (63,8%).
Conclusion. The theoretical knowledge of modern students about potential medical and social problems and risks of EBW and/or obesity does not guarantee a healthy lifestyle as a daily practice. This is most likely due to a conscious choice.
ANALYSIS OF MODERN DATA
What is already known about the subject?
- Smoking, including using electronic nicotine delivery systems, is not only a bad habit, but also a form of addiction.
- Nicotine addiction complicates the control of existing noncommunicable diseases, in particular respiratory diseases.
What might this study add?
- The neurobiological mechanisms of nicotine addiction are analyzed, including the role of molecular genetic and epigenetic changes.
- Key treatment methods are highlighted, including nicotine replacement therapy, pharmacological approaches (varenicline, cytisine) and promising non-drug methods.
- Focus is on the need for further research to improve the effectiveness of existing approaches and develop novel strategies.
Aim. To analyze modern studies on most effective therapeutic approaches to the treatment of nicotine addiction by generalizing data on promising methods and strategies for their use.
Material and methods. The data from studies was generalized, in which the neurobiological pathogenesis of nicotine addiction and possible ways to solve this problem were analyzed. The search was carried out using the following keywords: "nicotine", "vaping", "epigenetics", "nicotine addiction", "nicotine replacement therapy", "electronic nicotine delivery systems" in the titles of publications, abstracts, keywords of articles in journals published in the period from January 1 2020 to October 1, 2024 and posted in following electronic bibliographic databases: PubMed, Сochrane Library, eLIBRARY. At the second stage, the received publications were evaluated according to the inclusion and exclusion criteria. At the final stage, a detailed study of the found publications in the compiled sample was carried out for new mechanisms of nicotine addiction formation and possible treatment methods.
Results. In publications posted and summarized in the above electronic bibliographic databases, special attention is paid to the molecular genetic mechanisms leading to neural adaptation and disease development. A new possible way to solve the problem is proposed — non-invasive brain stimulation.
Conclusion. The factual data on the pathogenesis of nicotine addiction are summarized, indicating that the participation of molecular genetic mechanisms in nicotine addiction is currently being actively discussed. Special attention is paid to neuroadaptation. Additional research is needed to analyze novel therapeutic tactics that involve non-invasive brain stimulation.
GUIDELINES
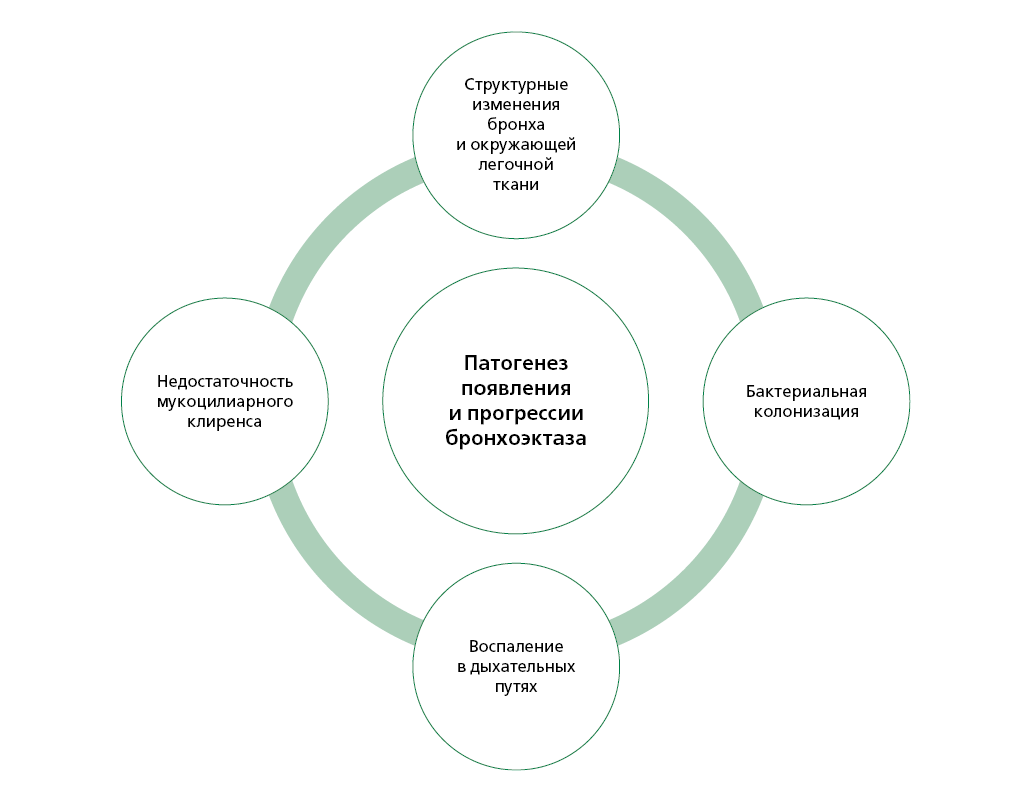
Follow-up of patients with bronchiectasis at various age stages shows that even with a favorable course of the disease, clinical improvement, lung morphological abnormalities do not regress, are the basis for exacerbations and chronicity of bronchopulmonary inflammation. Outpatient follow-up is the main approach to the prevention and early diagnosis of exacerbations, complications and progression of the disease, and the implementation of medical rehabilitation. The guidelines contain a description of the algorithm for appointment of bronchiectasis patients by a general practitioner and supporting materials. The guidelines are intended for general practitioners (family doctors), as well as for mid-level health providers working with the above-mentioned doctors, for paramedics performing the doctor functions, pulmonologists and other medical specialists involved in the management of patients with bronchiectasis, for heads of primary health care facilities.
МЕТОДИЧЕСКИЕ РЕКОМЕНДАЦИИ
The guidelines describe the management of outpatient follow-up by a general practitioner of patients with esophageal diseases (esophagitis, gastroesophageal reflux disease, Barrett’s esophagus and achalasia cardia). The following is presented: an approximate scope and frequency of paraclinical investigations, information on the diagnosis, treatment and prevention of complications of diseases. The guidelines are intended for general practitioners, family doctors, as well as for mid-level health providers working with the above-mentioned doctors, for paramedics performing the doctor functions. The guidelines can be used by public health physicians, heads of primary health care facilities and their divisions.
ISSN 3034-4565 (Online)