EXPERT COUNCIL
Division of the professional competencies of doctors and pharmacists is especially relevant due to increasing seeking medical advice by population from a pharmacy rather than a medical organization. This trend is driven by a shortage of physicians, difficulties in scheduling appointments, and long waiting times for consultations. Pharmacists are forced to go beyond their competencies, posing risks both to patients and to the professionals themselves, who are not authorized to diagnose diseases or prescribe treatments. The easy accessibility of overthe-counter medications, the vast amount of online health information, and aggressive pharmaceutical advertising contribute to the misconception that a physician’s consultation is not essential before taking medications. Selfmedication increases the risk of adverse reactions and severe consequences. Therefore, doctors and pharmacists must collaborate to address this issue.
Lack of communication between specialists is another challenge. Physicians prescribe treatments without always considering the availability, cost, and alternatives of medications in pharmacies. In turn, pharmacists may suggest substitutions without a complete understanding of the patient’s clinical condition. In addition, their legal status in consulting is limited, since they can only inform about pharmacy products, which limits their role in disease prevention. On December 19, 2024, as part of the International Congress "Therapy and Preventive Medicine", the All-Russian Conference "Doctors and Pharmacists: Colleagues or Competitors?" was held. Experts discussed pressing issues and proposed solutions. The key theses of the Expert Council’s resolution are presented in this article.
The document represents an expert consensus on the organizational and practical aspects of managing outpatients with prediabetes. The resolution emphasized the importance of timely detection and outpatient monitoring of individuals with carbohydrate metabolism disorders. We discussed diagnostics using various methods (fasting plasma glucose, HbA1c, oral glucose tolerance test), and the need to integrate the Finnish Diabetes Risk Score (FINDRISC) into the practice of preventive and outpatient monitoring examinations. The experts noted the lack of regulatory framework for prediabetes and emphasized the need to develop an interdisciplinary consensus on this condition. Proposals were made to amend statistical data forms, include prediabetes in the outpatient monitoring system, and develop a separate charge for in-depth preventive counseling. The discussion ended with the development of a set of proposals aimed at increasing the effectiveness of prevention, early diagnosis and medical monitoring of patients with prediabetes.
ANALYSIS OF MODERN DATA
How do regulatory changes in 2025 affect the primary health care management in Russia?
- The changes are aimed at improving the healthcare quality and accessibility, creating a more flexible system for managing primary health care, as well as introducing novel technologies and standards, which allows for a better response to the population needs.
What are the main reform areas in healthcare reflected in the new regulations?
- The main areas of change include increasing funding for healthcare, emphasizing the social responsibility of the healthcare system, introducing clinical guidelines, and improving the working conditions of health professionals, which contributes to improving the healthcare quality.
Aim. To analyze and assess changes in the legislation of the Russian Federation related to primary health care for the first quarter of 2025.
Material and methods. The study included an analysis of regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation that entered into force in the first quarter of 2025, as well as methodological guidelines. The analysis identified key changes related to the structure and functioning of the primary health care system, and assessed their impact on healthcare provision. Particular attention was paid to aspects related to improving the availability and quality of healthcare, as well as changes in management and financial mechanisms. This allows for a deeper understanding of the consequences of legal innovations for all healthcare participants.
Results. The study results showed that legislation changes create preconditions for more efficient functioning of the primary health care system in the Russian Federation. This, in turn, should improve public health and increase patient satisfaction.
Conclusion. The conducted study of legislation changes coming into force in the first quarter of 2025 and methodological guidelines emphasizes the importance of legal innovations in the primary health care system in the Russian Federation. The identified changes are aimed at improving the healthcare availability and quality, introducing modern technologies and improving the qualifications of medical workers. These measures create favorable conditions for work of health facilities and increase patient satisfaction. Thus, legal reforms represent an important step towards improving the healthcare system, which ultimately should contribute to improving public health and increasing healthcare efficiency.
The modern concept of a personalized approach to studying the relationship between diseases contributes to an in-depth multimorbidity study. Asthma is one of the most common pathologies among chronic respiratory diseases, characterized by wide heterogeneity and high comorbidity, especially with cardiovascular diseases in the older age group. Due to the difficulties of differential diagnosis of these diseases and their mutually aggravated course, measures for the prevention of heart failure (HF) in asthma patients should be structured.
The aim of the review was to highlight the etiology, similarity of the clinical performance and common pathogenesis links in patients with HF and asthma, as well as the main approaches to the prevention of heart failure in patients with asthma.
The review summarizes recommendations for the prevention of HF and outpatient follow-up of asthma patients for the timely diagnosis of HF.
What is already known about the subject?
- Cytolysis is a common diagnostic finding in the clinical practice of a physician. The main task for a doctor is to determine the origin of increase transaminase levels, establish the scope of additional examination and prescribe adequate treatment.
What might this study add?
- The most common causes of cytolysis, including those of non-hepatic origin, are analyzed.
- The diagnostic minimum for differential diagnosis of liver diseases accompanied by an aminotransferase increase in the peripheral blood has been determined.
Aim. To study the main causes of increased aminotransferase levels in the practice of a primary care physician.
Material and methods. The scientific literature was analyzed using the PubMed and eLIBRARY.RU databases by following keywords: cytolysis syndrome, aminotransferases, hypertransferasemia, increased alanine aminotransferase, increased aspartate aminotransferase. Based on the literature search, data on the most common cytolysis causes in clinical practice were analyzed and systematized, and a step-by-step algorithm for diagnostic search was presented.
Results. In clinical practice, cytolysis syndrome can be detected both among patients with existing complaints from the digestive system at the time of examination, and in asymptomatic patients (random diagnostic finding during a preventive medical examination).
Conclusion. To determine the strategy of managing a patient with cytolysis, the etiological factor should be clearly and accurately verified, which sometimes requires a long time and routine expensive research methods.
GUIDELINES
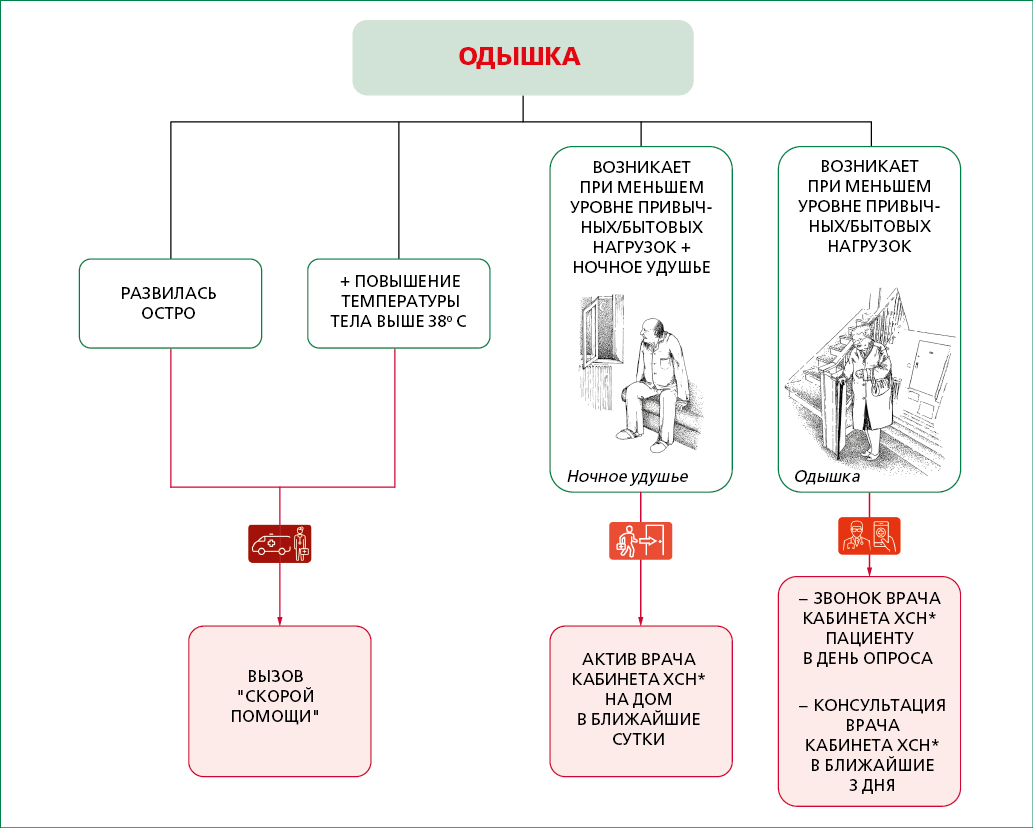
Outpatient follow-up in primary care is one of the resources for reducing mortality from diseases of the circulatory system and increasing life expectancy. These guidelines contain a description of current issues related to the organization of outpatient follow-up of patients with chronic heart failure by a general practitioner.
The guidelines are intended for district internists, general practitioners (family doctors), district internists of the shop medical district, as well as for secondary medical personnel working with these doctors, for paramedics of paramedic-obstetric stations (paramedic health centers) in case they are assigned the functions of the attending physician.
The guidelines can be used by public health physicians, heads of primary health care facilities and their divisions.
The guidelines describe the organization of follow-up of patients with alcohol-associated liver cirrhosis by a general practitioner.
This document presents modern approaches to diagnostics, including clinical and paraclinical methods necessary for follow-up monitoring of patients with alcohol-associated liver cirrhosis. It also includes treatment standards covering both pharmacological and non-pharmacological methods aimed at slowing the disease progression, preventing complications and improving the quality of life. Special emphasis is placed on the integration of a multidisciplinary approach, involving collaboration among specialists to optimize patient management. The guidelines are based on evidence-based medicine and include the latest clinical research and international standards, making them relevant and useful for practitioners.
The guidelines are intended for general practitioners, family doctors, as well as for mid-level health providers working with the above-mentioned doctors, for paramedics performing the doctor functions. The guidelines can be used by public health physicians, heads of primary health care facilities and their divisions.
Chronic bronchitis is the most common disease from the group of chronic respiratory diseases. Follow-up monitoring of patients with chronic bronchitis is the main approach to the prevention and early diagnosis of exacerbations, complications, progression and transformation into other diseases (for example, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease), as well as to the implementation of medical rehabilitation. The guidelines contain a description of the algorithm for outpatient appointment of patients with chronic bronchitis by a general practitioner and the auxiliary materials.
The guidelines are intended for general practitioners, family doctors, as well as for mid-level health providers working with the above-mentioned doctors, for paramedics performing the doctor functions. In addition, it can be useful for pulmonologists, allergists/immunologists and other medical specialists involved in the management of patients with chronic bronchitis, for heads of medical organizations (structural divisions of medical organizations) providing primary health care.
ISSN 3034-4565 (Online)