NATIONAL HEALTHCARE SYSTEMS
What is known about the subject of the study?
- In the member States of the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the development of primary health care (PHC) is given top priority, and digitalization is used as a mechanism to improve the efficiency and quality of its provision.
- The CIS countries under study have adopted and are implementing strategies (or similar regulatory acts) and programs for the digitalization of primary health care information systems (IS) based on the introduction of electronic medical records with subsequent integration with other IS.
- Digital technologies, including telemedicine, are being actively implemented in primary health care, becoming a familiar tool in the provision of primary health care, dynamic monitoring, and preventive medicine for both healthcare professionals and patients.
What do the research results add?
- An analysis of the characteristics of the digitalization aspect of PHC in the CIS countries has shown differences in the degree of digitalization and integration of their PHC, which affects the readiness of health systems to permanently provide PHC to attached residents in managing their health throughout their lives.
- The similarity of the ways of developing the digitalization of PHC IP in the Commonwealth and the IP of healthcare systems in general, revealed during the review, determined the prospects for combining the efforts of countries to harmonize regulatory and reference information on healthcare for the development of IP.
TERRITORIAL FEATURES OF THE PRIMARY HEALTH CARE
What is already known about the subject?
- One of the priority tasks facing the healthcare system is to eliminate territorial differences in healthcare availability and reduce inequalities in its provision.
What might this study add?
- Practical experience in the implementation of technologies aimed at improving health care in hard-to-reach and sparsely populated regions of the Russian Federation was analyzed.
Aim. To summarize the experience of the Sakha Republic (Yakutia) in improving the healthcare management in remote, hard-to-reach and sparsely populated areas.
Material and methods. We used data from analytical and statistical reports of the Republican Center of Mobile Teams of the Sakha Republic (Yakutia) for 2022-2024, as well as regulatory documents on the primary healthcare (PHC) management in hard-to-reach regions.
Results. The article considers current problems and directions for improving the availability of PHC to residents of hard-to-reach Arctic areas of the Sakha Republic (Yakutia). It is shown that the Republican Center of Mobile Teams, which has been operating since 2023, effectively solves the problems of healthcare provision in remote areas without involving the personnel and material and technical resources of the leading republican medical organizations. The mobile medical teams operating in the Arctic area of the republic are responsible for the following: assessing the population health status, including the nomadic routes of residence of indigenous peoples of the North; early diagnosis of noncommunicable diseases; identifying patients in need of specialized, including high-tech care; imaging follow-up monitoring, including the use of telemedicine consultations.
Conclusion. Maintaining and strengthening the population health in Arctic areas of the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia) is a complex multifaceted task that requires significant resources and interdepartmental cooperation. In the conditions of a harsh climate, scattered settlements and low transport accessibility, providing the population with affordable and high-quality health care requires the development of a specialized area — Arctic medicine.
ORGANIZATION OF PREVENTIVE CARE TO THE POPULATION
What is known about the subject of the study?
- Type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM) is one of the most common chronic non-communicable diseases characterized by high medical and social significance and economic burden.
- Effective follow-up and early diagnosis of type 2 diabetes are recognized as key measures in international strategies to combat noncommunicable diseases.
- Primary health care plays a central role in the management of type 2 diabetes, providing long-term support, coordination of care and monitoring of patients’ condition.
What does this study add?
- A systematic analysis of international models of early detection and follow-up of patients with type 2 diabetes is presented, including practices in Europe, North America, East Asia and the countries of the Commonwealth of Independent States.
- The key elements of effective type 2 diabetes control systems are highlighted: screening, digital support, interdisciplinary teams, patient education.
- Proposals have been formulated to adapt international practices in the countries of the Commonwealth of Independent States, taking into account the specifics of their healthcare systems, the availability of resources and the level of digitalization.
- The prospect of introducing modern digital solutions and medical decision support systems to improve the quality and effectiveness of monitoring was noted.
LEGAL ASPECTS OF PRIMARY HEALTH CARE
- How do legislative changes in 2025 affect the management and provision of primary health care in Russia?
- The changes are aimed at improving the quality and accessibility of medical services, introducing novel technologies (for example, telemedicine), optimizing document flow and standardizing processes. They also include the mandatory use of clinical guidelines, which increases the responsibility of health workers and the quality of care.
Aim. A comprehensive study and assessment of legal changes in the Russian Federation concerning the management and provision of primary healthcare (PHC) for April and May 2025.
Material and methods. The study included a study of regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation published in April and May 2025, as well as law enforcement innovations of the Review of Judicial Practice of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation. The author’s analysis identified significant transformations in the organizational and functional structure of PHC system, including an assessment of their impact on clinical practice and dynamic processes of medical services delivery. The study placed particular emphasis on studying the factors determining the increase in the availability and quality of healthcare.
Results. The study shows that the legal changes introduced form the institutional prerequisites for optimizing PHC functioning in Russia, creating conditions for strengthening the public health structure and increasing the efficiency of care. The data obtained suggest that the implementation of these regulatory innovations will contribute not only to improving key public health indicators, but also to increasing the level of patient satisfaction with the quality of care. This in the long term can lead to improvement in the healthcare system as a whole.
Conclusion. Analysis of the legal trends and the Review of Judicial Practice of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation, adopted (published) in April and May 2025, shows their significant impact on the transformation of PHC system in Russia. The study revealed that key procedural and institutional innovations are aimed at ensuring wide healthcare accessibility, introducing innovative diagnostic and treatment technologies, as well as systematically improving the professional level of medical personnel. The implementation of these measures creates institutional prerequisites for high-quality modernization of medical institutions, which objectively leads to an increase in the standards of care and an increase in patient satisfaction. The legislative initiatives under consideration create a conceptual basis for the progressive development of Russian healthcare aimed at achieving a sustainable improvement in public health indicators and optimizing the healthcare system.
DEVELOPMENT OF DIAGNOSTIC AND TREATMENT METHODS
- Elderly and senile age is a proven risk factor for antibiotic-associated diarrhea, including that caused by C. difficile.
- To prevent complications, composition of the gut microbiota should be improved after antibacterial therapy.
- Immunocompromised patients are recommended therapy based on metabolites of probiotic strains without live microorganisms.
Aim. To evaluate the effectiveness of the Bactimunal® metabiotic complex (active metabolites of Bacillus subtilis) in the treatment regimens of antibiotic-associated diarrhea (AAD) in elderly and senile patients.
Material and methods. The study involved 42 patients from a multidisciplinary hospital aged 65 to 90 years with a diagnosis of AAD. Patients in the main group (n=27) received the Bactimunal® metabiotic complex 1 capsule 2 times a day for 28 days in addition to standard AAD therapy; patients in the control group (n=15) did not receive metabiotic support during AAD therapy. In all patients of the main and control groups, the clinical condition, severity of gastrointestinal symptoms, stool frequency and consistency, laboratory test data were assessed at the beginning of the study and after 28 days. Colonoflor-16 method was used to assess the colon microbiocenosis.
Results. The clinical performance of AAD in elderly and senile patients was dominated by diarrheal syndrome with increased stool frequency up to 4-6 times a day without hematochezia. C. difficile toxins A and B were detected in 44,4% of patients. According to the Colonoflor-16 test, a decrease in the total bacterial count was revealed, mainly due to Bifidobacterium spp. (100%) and Lactobacillus spp. (77,7%). With Bactimunal® metabiotic complex therapy, the repeated study revealed a decrease in the number of bowel movements and a tendency to normalize stool consistency, an increase in Lactobacillus spp. (in 40%), a tendency to increase in Bifidobacterium spp. (50,2%), compared with the control group.
Conclusion. The administration of the Bactimunal® metabiotic complex 1 capsule 2 times a day for 28 days demonstrated an increase in obligate microbiota, a decrease in the number of bowel movements and a tendency to normalize stool consistency.
- Biliary hypertension syndrome requires high clinical alertness, as it can be a manifestation of numerous digestive system diseases.
- A case of a 46-year-old patient is presented, in whom biliary hypertension syndrome arose as a result of a rare pathology — major duodenal papilla adenoma.
- The complexity of verification of major duodenal papilla adenoma is demonstrated, despite the use of highly informative diagnostic methods.
Introduction. Major duodenal papilla (MDP) adenomas are rare, up to 0.2-1.0% of all tumors of the gastrointestinal tract. Their diagnosis is often difficult, which is clearly reflected in the presented case.
Brief description. A 46-year-old patient fell ill acutely in September 2024 with a picture of acute respiratory disease. After two courses of antibacterial therapy, jaundice, skin itching, cytolysis and cholestasis syndromes appeared. The patient was observed with a diagnosis of drug-induced hepatitis with a moderate positive effect from hepatotropic therapy. In December 2024, symptoms relapsed, and the patient was hospitalized in one of the city hospitals, where viral, autoimmune liver diseases, liver vascular thrombosis, and cardiovascular pathology were ruled out. According to the abdominal ultrasound, pancreatic hypertension was detected. When Contrast-enhanced abdominal computed tomography revealed biliary hypertension with suspected choledocholithiasis, stenosis of the common bile duct terminal part, which were subsequently not confirmed by magnetic resonance imaging. Major duodenal papilla adenoma was suspected and confirmed by histological examination during repeated gastroscopy, 5 months after the disease onset.
Discussion. The presented case demonstrates the pathological process at all stages, the results of numerous diagnostic studies used to verify the diagnosis, a list of nosological units and a discussion of their probability in the context of differential diagnostics.
PROVIDING MEDICAL CARE TO VARIOUS GROUPS OF THE POPULATION
The guidelines describe the management of outpatient follow-up of patients with gastric and duodenal ulcer by a primary care physician. The following are presented: the approximate scope and frequency of paraclinical examinations, information on the diagnosis, treatment and prevention of complications of the disease. The guidelines are intended for district internists, general practitioners (family doctors), district internists of the shop medical district, as well as for secondary medical personnel working with these doctors, for paramedics of paramedic-obstetric stations (paramedic health centers) in case they are assigned the functions of the attending physician.
The guidelines can be used by public health physicians, heads of primary health care facilities and their divisions.
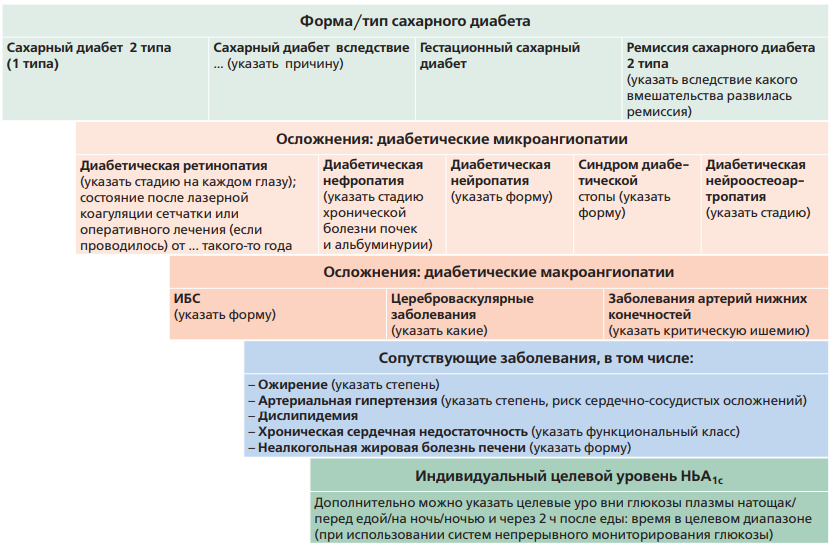
The guidelines outline modern approaches to the diagnosis and treatment of type 2 diabetes, including clinical and paraclinical methods necessary for effective monitoring of patients’ condition. Key attention is paid to outpatient follow-up. Both drug and non-drug treatment methods are presented, aimed at preventing the progression of diabetes, reducing the risk of complications and improving the quality and duration of life of patients. Algorithmization and structuring of modern clinical guidelines and standards in terms of outpatient follow-up make the document relevant, practice-o riented and useful for health professionals. The inclusion of evidence data ensures the high efficiency of the proposed approaches and their application in routine health practice.
The guidelines are intended for district internists, general practitioners (family doctors), district internists of the shop medical district, as well as for secondary medical personnel working with these doctors, for paramedics of paramedic- obstetric stations (paramedic health centers) in case they are assigned the functions of the attending physician.
The guidelines can be used by public health physicians, heads of primary health care facilities and their divisions.
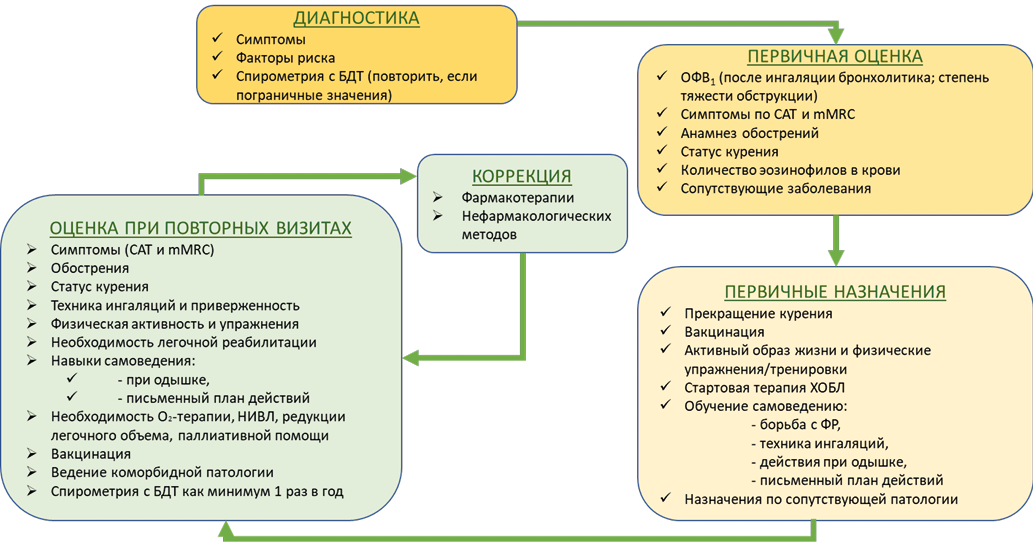
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) ranks high among chronic respiratory diseases, including as a cause of death. COPD is associated with the risk of other diseases with unfavorable prognosis, including cardiovascular ones. Outpatient monitoring of patients with COPD is the main approach to the prevention and early diagnosis of exacerbations, complications and progression of the disease, the implementation of medical rehabilitation and early diagnosis of comorbid pathology. The guidelines describe the algorithm for outpatient consultation of patients with COPD by a primary care physician and supporting materials.
The guidelines are intended for district internists, general practitioners (family doctors), district internists of the shop medical district, as well as for secondary medical personnel working with these doctors, for paramedics of paramedic-obstetric stations (paramedic health centers) in case they are assigned the functions of the attending physician.
The guidelines can be used by public health physicians, heads of primary health care facilities and their divisions.
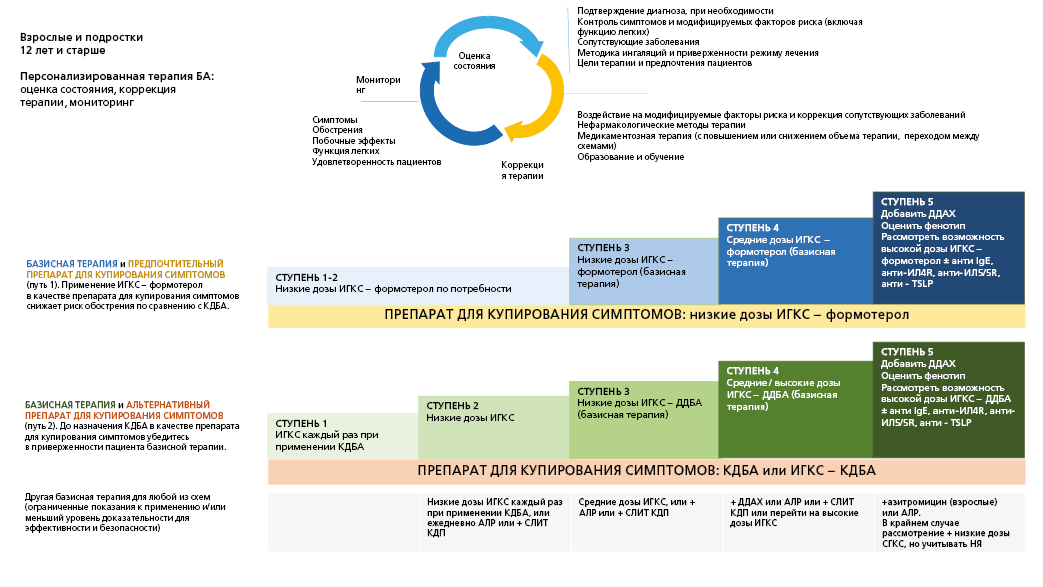
Most patients with asthma respond well to treatment, but some of them have a disease that is difficult to control. This may be due to a number of factors, such as the presence of triggers (allergens, smoking, etc.), disease phenotype, severe airway remodeling (and, as a result, fixed obstruction), low adherence to treatment, and improper inhalation technique. Such patients have a high frequency of exacerbations and requests for care, risk of complications. In addition, patients with asthma of any course, including mild, may have severe exacerbations. Outpatient follow-up of patients is the main approach to the prevention and early diagnosis of exacerbations, complications and progression of the disease, and the implementation of medical rehabilitation. The guidelines describe the algorithm for outpatient appointment of patients with asthma by a primary care physician and supporting materials.
The guidelines are intended for district internists, general practitioners (family doctors), district internists of the shop medical district, as well as for secondary medical personnel working with these doctors, for paramedics of paramedic-o bstetric stations (paramedic health centers) in case they are assigned the functions of the attending physician.
The guidelines can be used by public health physicians, heads of primary health care facilities and their divisions.
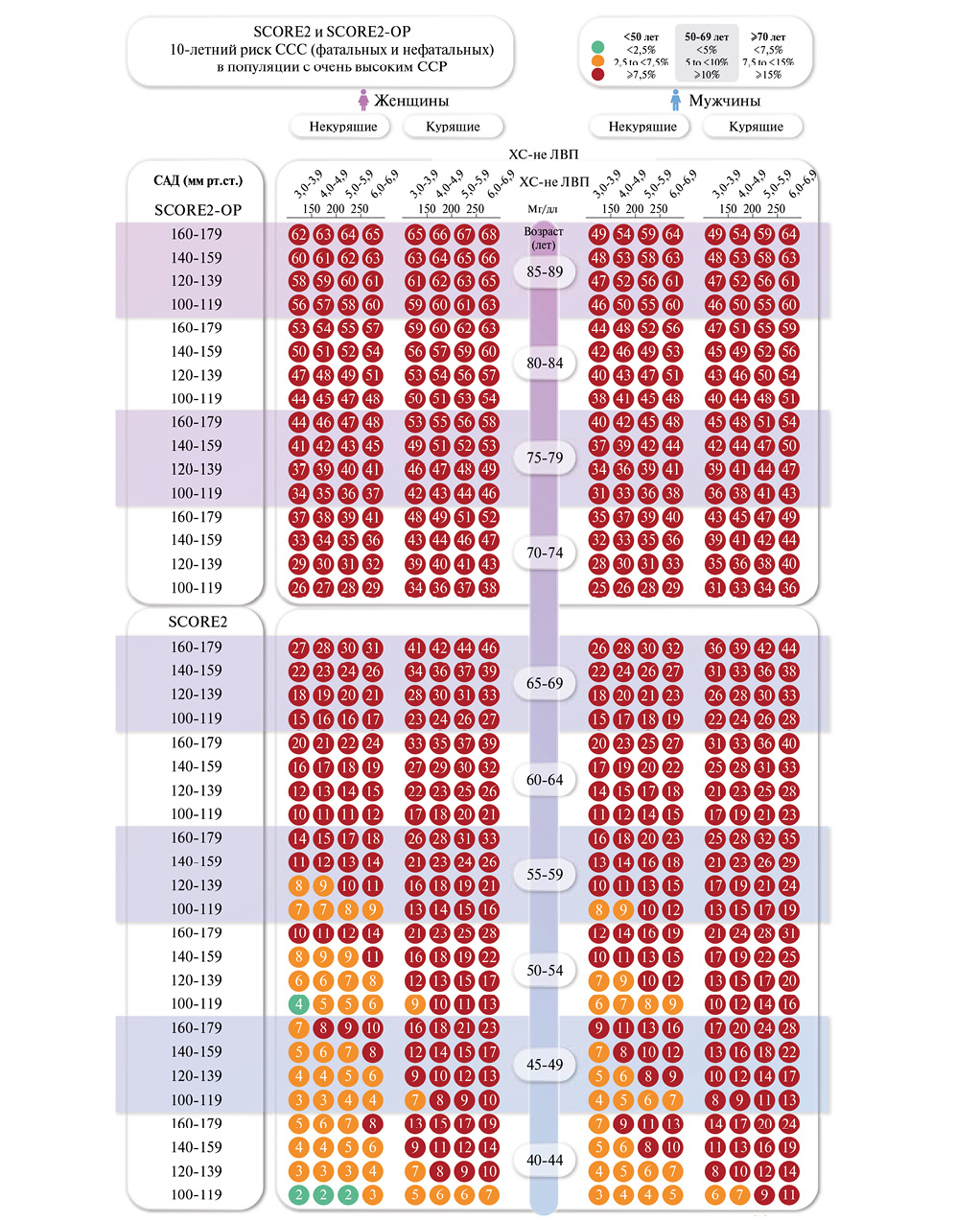
The guidelines have been developed to standardize and optimize approaches to the follow-up of hypertensive outpatients. They are based on the latest Russian clinical guidelines, standards and procedures for the healthcare provision. Key attention is paid to outpatient follow-up, risk factors, prevention of complications, as well as drug and non-drug treatment.
The guidelines present algorithms for outpatient follow-up, methods for blood pressure monitoring, criteria for drug and non-drug therapy prescription, as well as approaches to medical rehabilitation. Particular attention is paid to an individualized approach, adherence to therapy, monitoring the effectiveness of treatment and interdisciplinary interaction.
The guidelines are intended for district internists, general practitioners (family doctors), district internists of the shop medical district, as well as for secondary medical personnel working with these doctors, for paramedics of paramedic- obstetric stations (paramedic health centers) in case they are assigned the functions of the attending physician.
The guidelines can be used by public health physicians, heads of primary health care facilities and their divisions.
ISSN 3034-4565 (Online)