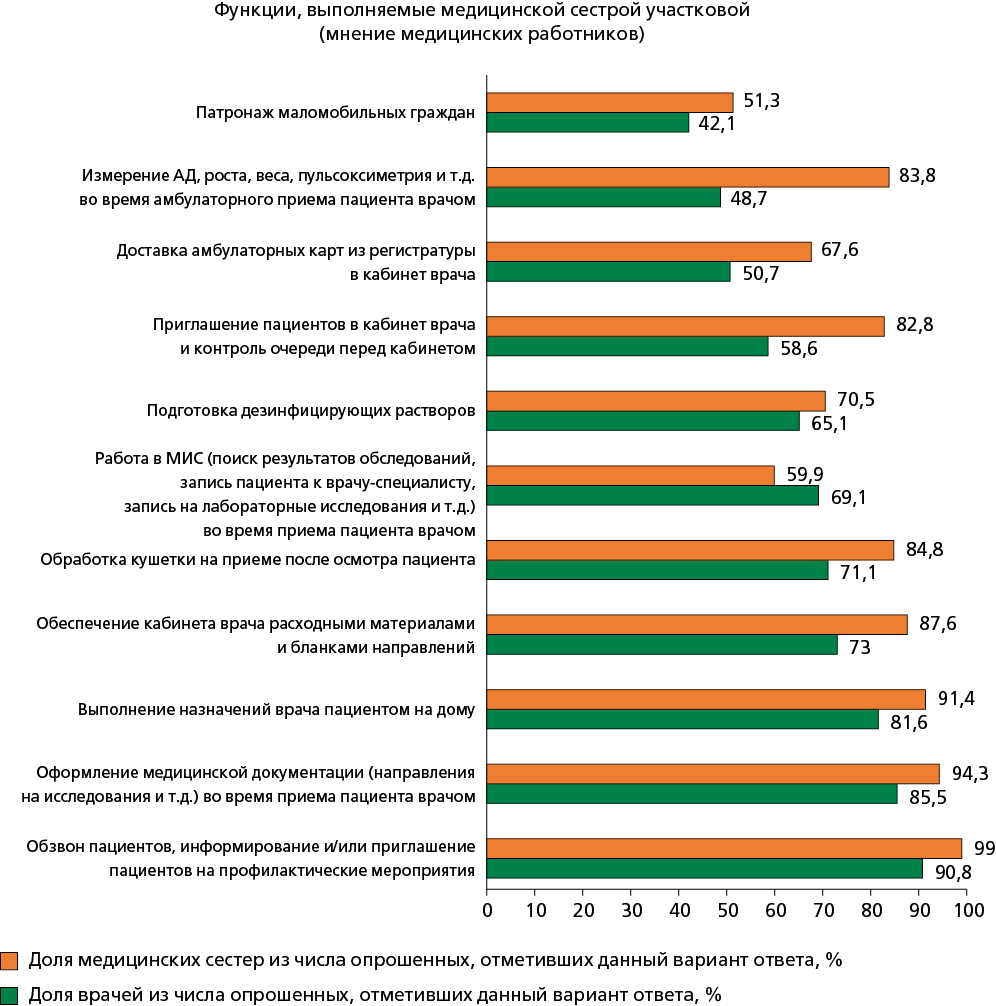NATIONAL HEALTHCARE SYSTEMS
What is already known about the subject?
- Primary health care (PHC) provides the first contact of the population with the health care system, close to the place of residence, meets the basic human health needs.
- The special attention of governments and researchers to PHC is due to the importance of the development of each of its aspects: organizational, management, resources, financing, digitalization and results for improving public health.
What might this study add?
- In the organization of health systems of the member states of the Commonwealth of Independent States, similar principles and characteristics have been preserved; in addition, new organizational decisions affecting the development of PHC have been analyzed.
The article based on an analytical review of information sources on the status and development of various aspects of primary health care (PHC) in the world and in selected countries, as well as international evidencebased recommendations, to assess the prospects of using international experience and recommendations for the development of PHC in the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) member states with regard to the organizational aspect, which is considered in this article.
A database of scientific publications, regulatory legal documents, and Internet resources was used with an emphasis on evidence-based reviews and methodological documents that were included on the basis of selected keywords and concepts related to organization aspect of health systems and PHC and characteristics, as well as by the criteria of potential impact on the results of PHC provision. Priority in the search was given to materials from the last decade and to the countries with similar models of health systems.
The characteristics of the main aspects of national PHC subsystems — organizational, management, resources, financing, digitalization and results — were identified, systematized and ordered in the structure of the PHC characteristics matrices in the selected countries.
This two-part article presents results of an analysis of the development of the organizational aspect of PHC and its characteristics, including the implementation of recommendations selected in the review process with proven effectiveness in the CIS member states.
Analysis of the development since 2002 of the WHO idea of the transition of the PHC subsystem organization from the "radar" principle associated with the concept of "completed case of medical care" to the continuous and permanent management of patients with chronic diseases by a team of specialists, as well as the experience of the CIS member states in the medical examination of the attached population and dispensary supervision (implementation of management programs) for patients with chronic diseases gave reason to propose an updated name for the principle of constant medical care in managing people health throughout their lives — the principle of "permanence". And also suggest using it not only in the management of chronic conditions,
PRACTICAL WORK EXPERIENCE
What is already known about the subject?
- Providing health care people with disabilities requires providing conditions for an accessible environment in healthcare facilities and surroundings, the requirements for which are defined by numerous disparate documents.
What might this study add?
- Regulatory legal acts in terms of regulating the accessible environment in healthcare facilities have been systematized. In addition to technical conditions, a set of organizational solutions is needed, including regulations for employees responsible for distributing patient flows in the healthcare facilities and their interaction.
Provision of health care for persons with disabilities (PDs) requires additional conditions — creation of an accessible environment in medical facilities and surroundings.
Aim. To study principles of providing inclusive and safe environment for PDs in healthcare facilities providing primary health care.
Material and methods. A search and analysis of regulatory legal documents and statistical data on providing an accessible environment for PDs was conducted. Data from the official websites of the Federal State Statistics Service and the Russian Public Opinion Research Center were used. The search for regulatory legal acts was carried out using the reference legal system Consultant Plus. The following research methods were used: descriptive statistics, content analysis.
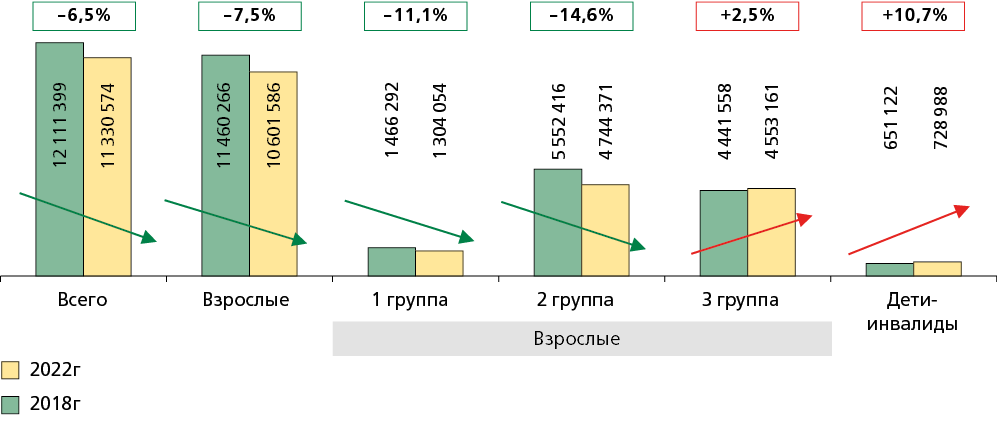
Results. The tendency towards an increase in the number of people with repeated disability and the number of disabled children allows to predict a further increase in the number of disabled persons in adulthood. Accessibility and inclusive conditions are a prerequisite for such patients visiting primary health care facilities. The requirements for them are regulated by a large number of guidelines, which were systematized within the study.
Conclusion. The increase in the number of PDs determines the relevance of creating an inclusive environment taking into account the needs of people with various health and mobility impairments. In addition to creating technical conditions for a inclusive and safe environment, a set of organizational solutions is needed, including regulations for employees responsible for distributing patient flows in the healthcare facilities and their interaction. Federal state educational standards and typical job functions of employees of healthcare facilities (nurse, medical registrar, medical administrator) need to be revised in terms of specifying their participation in providing assistance to PDs.
What is already known about the subject?
- Recently, the issues of expanding the role of mid-level health professionals, including district nurses, have been actively studied, while normative legal acts regulate a wide range of their functions.
- The organization of independent work of a district nurse with the population can lead to an increase in the share of preventive measures in the structure of primary health care, and an increase in the population’s commitment to preventive measures.
What might this study add?
- The conducted studies rationale changing the content of a district nurse activities and the need to introduce new organizational solutions.
Aim. To justify a change in activities of a district nurse and the expansion of her clinical role.
Material and methods. An analysis of regulatory legal acts governing the organization of primary health care and the activities of a district nurse was conducted. A medical and sociological study was conducted — an anonymous questionnaire of district general practitioners, district nurses, patients and observations of the work of district general practitioners and district nurses in parallel in order to assess the activities of a district nurse in the current situation. Based on analysis of the data obtained, organizational solutions were developed with a change in the activities of a district nurse. An organizational experiment was conducted. The following methods were used: analytical, statistical, content analysis, organizational experiment.
Results. An analysis of regulatory legal acts showed that the functions of a district nurse include the implementation of a wide range of activities, but in practice many of them are not implemented. According to the survey results, the main functions of a district nurse were informing patients and inviting them to preventive measures (this function was noted by 90,8% of doctors and 99,0% of nurses) and preparing medical documentation at an appointment with a doctor (this function was noted by 85,5% of doctors, 94,3% of nurses and 45,4% of patients), which confirmed the results of observations. The organization of independent nursing appointments allowed to increase the effective time of the district nurse’s work with patients during an outpatient appointment from 14,2 to 49,5% and during a shift from 12,3 to 20,8%, as well as to reduce the functionally idle time during an outpatient appointment from 13,8 to 0% and during a shift from 10,7 to 2,4%.
Conclusion. Changes in the activities of the district nurse contribute to an increase in its importance in the formation of a healthy lifestyle of the population, in the prevention of noncommunicable diseases and is a promising direction for improving primary health care. In matters of ensuring the availability of healthcare care, the professional competencies of the nursing staff should be taken into account.
EXPERT COUNCIL
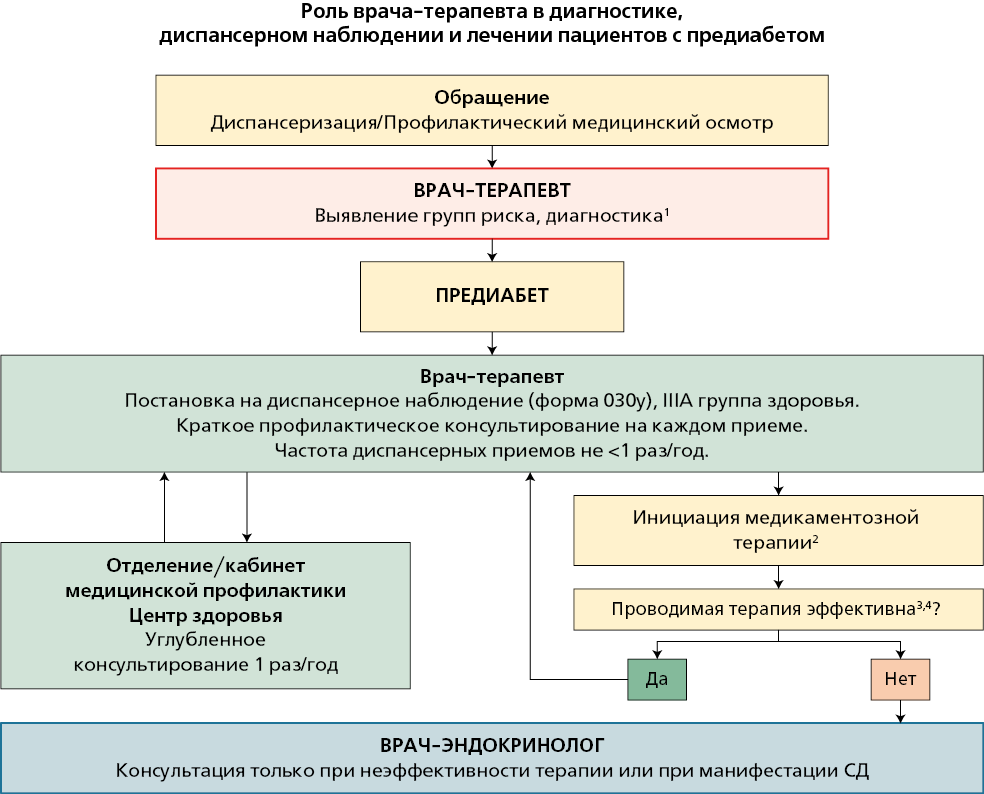
The steady increase in the prevalence of carbohydrate metabolism disorders worldwide, with the vast majority of type 2 diabetes (T2D), specifies the need to improve disease prevention measures. A special niche in the preventive continuum is occupied by early carbohydrate metabolism disorders, the treatment of which makes a significant contribution to T2D prevention. The absence of a characteristic clinical performance, inadequate apprehensive attitude of healthcare professionals contributes to unnoticed development of carbohydrate metabolism disorders, while progressive disorders lead to micro-, macrovascular complications and the manifestation of T2D. On September 16, 2024, under the chairmanship of Academician of the Russian Academy of Sciences O. M. Drapkina and under the aegis of the Russian Society for the Prevention of Noncommunicable Diseases, the Expert Council was held on Organizational and Applied Aspects of Follow-up Monitoring of Patients with Prediabetes by a General Practitioner. The meeting was attended by the main external experts in internal medicine of regional health protection executive authorities, leading experts of the National Medical Research Center for Therapy and Preventive Medicine and regional branches of the Russian Society for the Prevention of Noncommunicable Diseases, who presented current related problems and proposals for their solution. The Expert Council resolution is presented in this article.
SCIENTIFIC NOVELTY
What is already known about the subject?
- One of the important stages in the continuity between medical facilities of different levels is the change from outpatient conditions to a hospital or day hospital.
What might this study add?
- The definition of the concept of hospitalization in scientific sources, as well as in regulatory legal acts, is absent. At the same time, the authors agree that hospitalization is understood as placing a patient in a day hospital or inpatient facility.
Aim. To establish the essence, content and significant characteristics of the concept of hospitalization identified by various authors in publications from the electronic database Elibrary.ru, which is the basis of the Russian Science Citation Index.
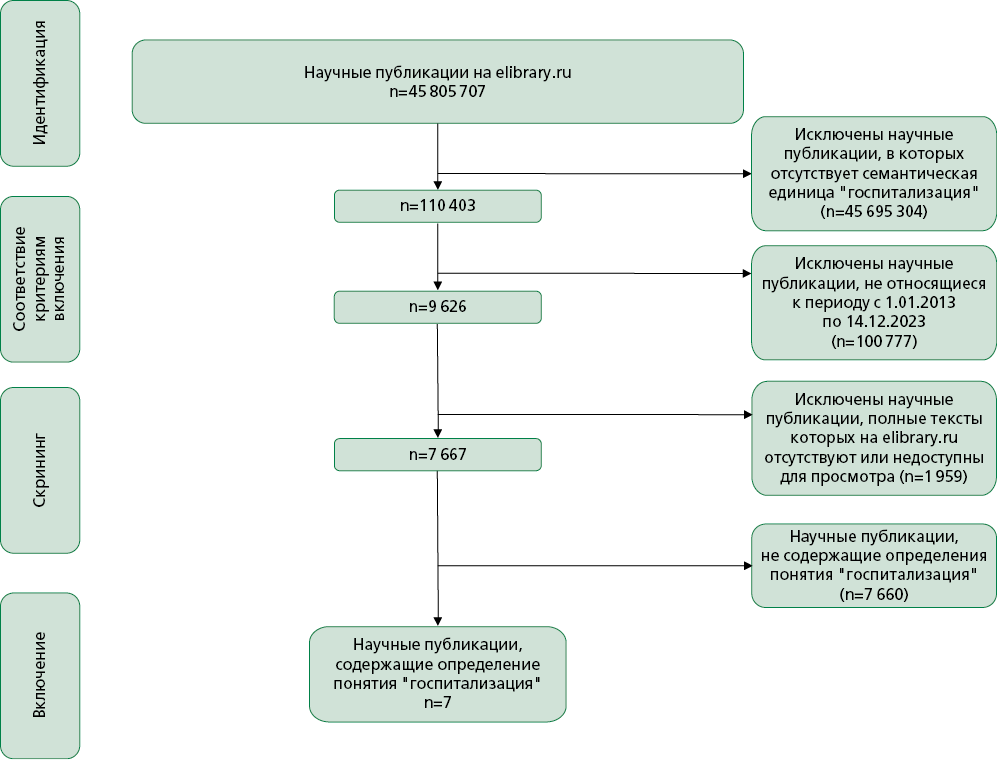
Material and methods. The search was carried out taking into account the morphological forms of the semantic unit "hospitalization" in the titles of publications, abstracts, keywords of articles in journals, books, conference proceedings, deposited manuscripts, data sets, dissertations, reports, patents, grants published in the period from January 1, 2013 to December 14, 2024 and posted in the Elibrary.ru database. At the second stage, the received publications were assessed according to the inclusion and non-inclusion criteria. At the final stage, a detailed study of the found publications in the compiled sample was carried out for the presence and disclosure of the concept of hospitalization.
Results. In publications posted and summarized in the Elibrary.ru database, the concept of hospitalization is understood, as a rule, as the admission of a patient for medical examination and treatment in a medical organization in inpatient settings, including a day hospital.
Conclusion. Establishment of the substantive, structural and functional characteristics of the concept of hospitalization, which have been identified by various authors, is a pressing scientific challenge. The work identifies further promising areas of scientific research.
GUIDELINES
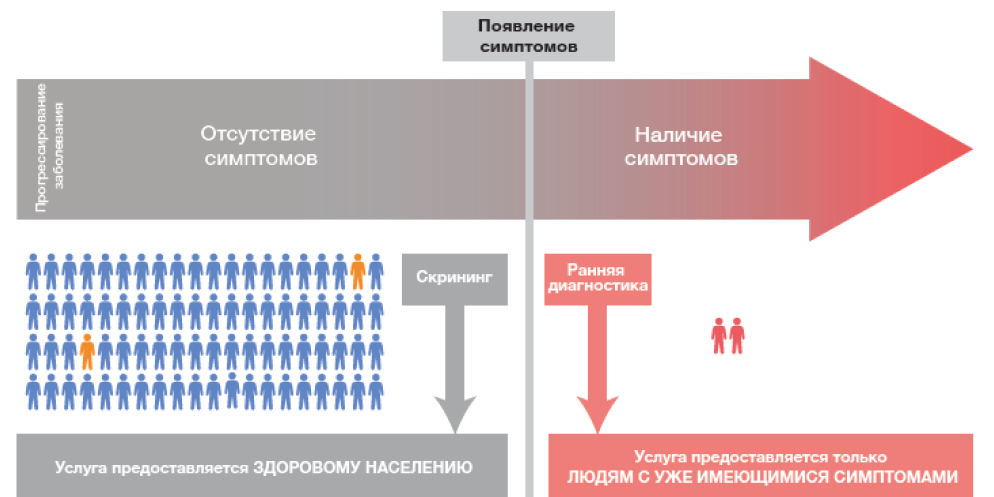
The Guidelines contain information on the theoretical foundations of screening for malignant neoplasms of the breast, regulatory legal acts regulating the organization of screening activities within the framework of medical examination of certain groups of the adult population, diagnostic algorithms and routing of the examined persons. Guidelines have been developed for the heads of medical organizations providing primary health care in terms of organizing processes, internists, general practitioners, medical workers from among the secondary medical personnel who are directly involved in the implementation of the process of medical examination of certain groups of the adult population.
The methodological recommendations have been developed with the aim of grading, systematizing and identifying key areas for the implementation of individual measures or a comprehensive corporate program for reproductive health promotion in working individuals at the employer level, including taking into account international experience.
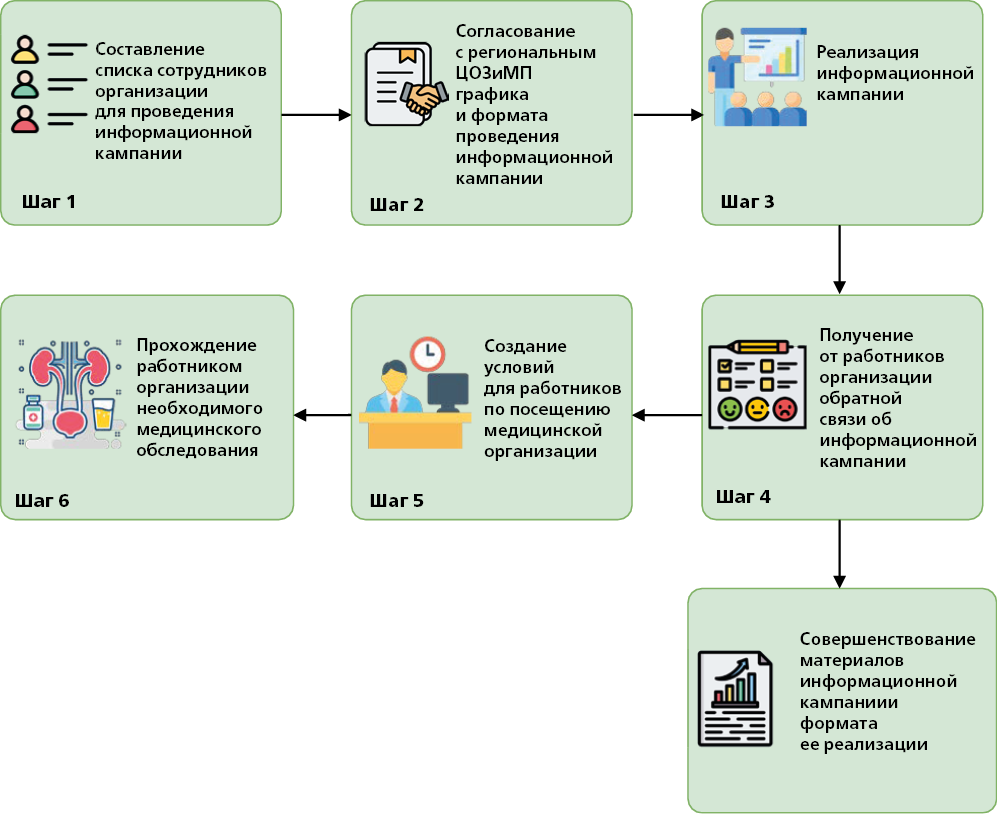
The guidelines describe seven key subprograms aimed at early diagnosis and timely treatment of urinary tract diseases, assessment of reproductive health, improving literacy in sex education and behavior, reducing the negative impact of industrial and external environmental factors on reproductive health, increasing commitment to measures to combat risk factors for noncommunicable diseases, providing support during menopause in women and andropause in men, and creating conditions in the workplace conducive to maintaining a strong family. The guidelines are intended for healthcare and public health organization specialists, heads of state authorities of constituent entities of the Russian Federation in the field of health protection, specialists of regional centers for public health and medical prevention, as well as for heads of organizations in various economic sectors. The materials presented in the guidelines can also be used by medical workers of various specialties (paramedics, general practitioners (family doctors), obstetrics and gynecology doctors, dermatology and venereology specialists, medical prevention doctors, occupational pathology physicians and urologists).
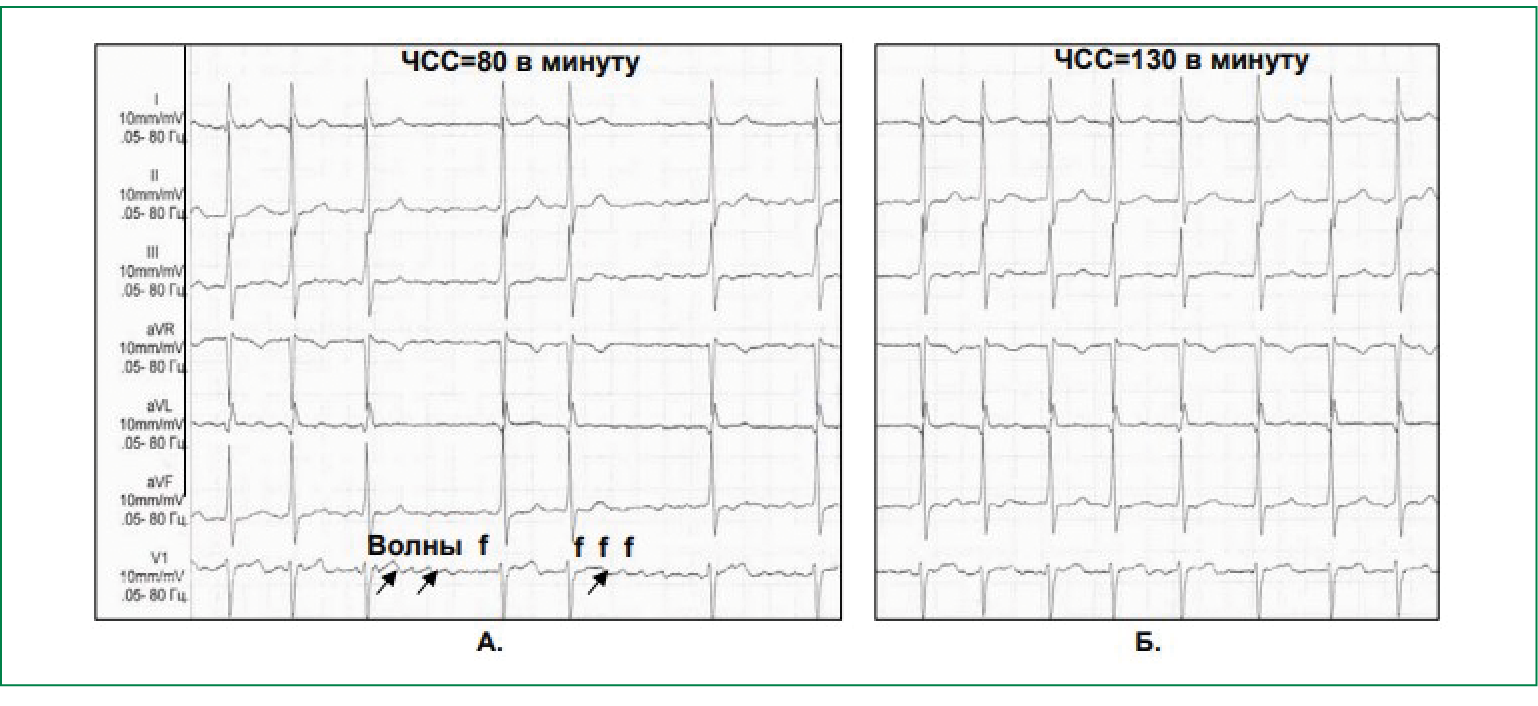
The guidelines contain a description of providing outpatient follow-up of patients with atrial fibrillation and flutter by a general practitioner, the approximate volume and frequency of paraclinical studies, information on the diagnosis and treatment of the disease, and the prevention of complications.
The guidelines are intended for district primary care physicians, general practitioners (family doctors), as well as for the nursing staff, for paramedics of the rural health posts if they are assigned the attending physician functions. The guidelines can be used by health professionals, heads of primary healthcare facilities and their divisions.
ISSN 3034-4565 (Online)